The term “Metaverse” originates from science fiction, particularly from Neal Stephenson’s 1992 novel “Snow Crash,” which referred to a virtual reality-based successor to the internet. A year before that, in 1991 in his novel “True Names”, Prof. Vernor Vinge, an American mathematician and computer expert, described a virtual realm accessible via a brain-computer interface, delivering an authentic sensory experience akin to the physical world. The metaverse is essentially a collective virtual shared space, created by the convergence of virtually enhanced physical reality and physically persistent virtual space.
In simpler terms, it’s a fully immersive digital world where people can interact with each other and digital objects in real time. Think of the book/movie “Ready Player One,” where the entire humanity is enjoying the simulation of virtual life – OASIS – with the help of VR visors and haptic gloves.
The metaverse is a developing virtual environment that brings together various technologies. This includes artificial intelligence, virtual reality, augmented reality, internet tech, blockchain, and digital twin technology. It’s not just about experiencing a digital world; it’s about socializing, working, playing, and conducting business within that digital realm.
While Ready Player One is about a world of 2045 (isn’t so far away, is it?), let’s talk about the metaverse technologies impacting the healthcare industry. Here are a few basic implementations to get us started:
- Remote consultations & therapy sessions
- Medical hands-on training simulations and experiences
- Pain management
- Exposure therapy
- Rehabilitation exercises
The metaverse blurs the lines between the digital and physical realities. As a result, it creates opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and interaction across industries.
State of Medical Technology in the Metaverse
Let’s consider the statistics of the metaverse in the healthcare market:
| Market revenue in 2023 | $9.5 billion |
| Projected revenue by 2028 | $79.6 billion |
| Revenue rate | The CAGR forecast is 52.9% |
| Market driver | The growing utilization of mixed reality in conducting minimally invasive surgeries. |
| Market opportunities | Greater integration of the metaverse into medical education and training. |
As we see from the statistics above, the rate at which the revenue is projected to grow is quite exponential and there are already healthcare institutions and major hospitals that are using the metaverse for medical purposes.
Existing Medical Metaverse Examples
Johns Hopkins Medicine
Johns Hopkins has been at the forefront of utilizing immersive technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) for various medical applications, including surgical planning, patient education, and therapy.
Cleveland Clinic
The Cleveland Clinic has integrated virtual reality into its medical training programs, allowing students and healthcare professionals to engage in realistic simulations of surgical procedures and patient care scenarios.
Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic has been exploring the use of augmented reality to assist surgeons during complex procedures, providing real-time guidance and visualization of critical anatomical structures.
Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH)
MGH has implemented virtual reality platforms for pain management therapies and psychological interventions, offering patients immersive experiences to alleviate discomfort and stress.
Stanford Medicine
Stanford has developed immersive technologies for medical education, leveraging virtual reality simulations to enhance learning experiences for students and improve their understanding of complex medical concepts and procedures. Another way of using AR/VR is helping patients get over the debilitating mental health issues.
Challenges and Opportunities of Metaverse
Developers encountering the integration of medical technology within the metaverse face several significant challenges, particularly concerning privacy concerns and data security. Here’s a deeper exploration of these challenges:

Privacy Concerns
Patient Data Protection: Ensuring the privacy of patient data is paramount. Medical information is highly sensitive and must be handled with extreme care to comply with regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the European Union.
Consent Management: Obtaining informed consent from users for the collection and processing of their health data within the metaverse presents a challenge. Developers must devise clear mechanisms for users to understand and consent to how their data will be used.
Identity Protection: Preventing unauthorized access to personal health records and protecting users’ identities within the metaverse is crucial. Developers need robust authentication and encryption measures to safeguard against identity theft and unauthorized data access.

Data Security
Cybersecurity Risks: The interconnected nature of the metaverse introduces cybersecurity vulnerabilities, such as data breaches, malware, and hacking attempts. Developers must implement robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, secure communication protocols, and regular security audits, to protect medical data from unauthorized access or manipulation.
Secure Transmission: Ensuring the secure transmission of medical data between virtual environments and external systems is essential. Developers need to employ encryption techniques and secure communication channels to prevent interception or tampering of sensitive information during transit.
Storage Protection: Safeguarding medical data stored within the metaverse or associated servers is critical. Developers should employ secure storage solutions, access controls, and data encryption to mitigate the risk of data breaches or unauthorized data retrieval.

Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to Healthcare Regulations: Developers must navigate complex regulatory frameworks governing the use and handling of medical data within the metaverse. Compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, and other regional data protection laws is necessary to avoid legal repercussions and maintain users’ trust.
Quality Assurance: Ensuring that medical technology within the metaverse meets regulatory standards for safety, efficacy, and accuracy is essential. Developers need to conduct thorough testing and validation processes to verify the reliability and integrity of virtual healthcare solutions.

User Trust and Acceptance
Ethical Considerations: Building trust among users regarding the confidentiality and integrity of their health data within the metaverse is essential. Developers must be transparent about their data handling practices, address ethical concerns, and prioritize user privacy to foster trust and acceptance of virtual healthcare technologies.
User Education: Educating users about the benefits, risks, and safeguards associated with medical technology in the metaverse is crucial. Developers should provide clear information and resources to empower users to make informed decisions and actively participate in managing their health data.
Future Trends and Predictions
The quality of medical care is an important factor in ensuring that our world survives. It involves both physical and mental health and provides sustainability for human development.
Several technologies play a critical role in crafting the healthcare metaverse in such a way that tackles the challenges above:
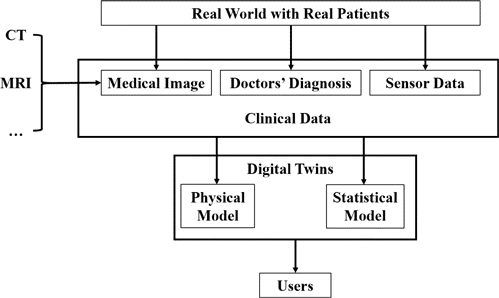
Digital Twins
In healthcare, a digital twin can represent different things, but it often focuses on a patient or a specific organ. Here’s a narrower explanation:
- Patient Focus: A digital twin can be a virtual model of a patient that incorporates their medical history, genetic data, wearable sensor data (like heart rate or activity levels), and other relevant information. This comprehensive picture allows doctors to:
- Personalize care: Tailor treatment plans based on the individual’s unique biology and response to medications.
- Predict health risks: Identify potential health problems before they arise and take preventive measures.
- Organ Focus: A digital twin can also represent a specific organ, like a heart or liver. This virtual organ would be based on medical scans, patient data, and real-time sensor information (if applicable). Doctors could use this to:
- Simulate procedures: Plan and test surgeries or other interventions virtually before performing them on a real patient.
- Optimize treatment: See how different medications or therapies would affect the virtual organ, helping choose the most effective course of action.
Digital twins in healthcare are about creating virtual representations that improve our understanding of individual patients and organs, leading to more personalized and effective care.
Check out our article on personalized medicine approaches.
Blockchain
We’ve talked about data security and privacy and protocols above. Metaverse is literally data in a visual form and it’s information about virtual objects’ parameters, users’ personal information, and general metaverse files, among a multitude of other things. One of the technologies that help in this case is blockchain.
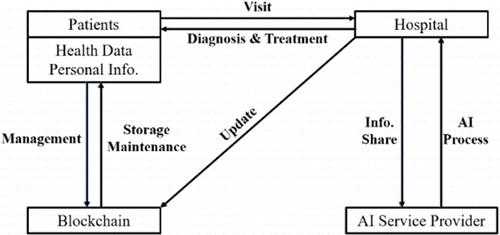
Blockchain is a chain storage structure that stores data in blocks (hence the word “block-chain”) and connects each block in chronological order, which ensures the correct track of the information and its ownership.
Blockchain offers several advantages for the healthcare industry, particularly in areas of data security, privacy, and accessibility.
Here’s how blockchain can be helpful:
- Secure Data Storage: Blockchain’s decentralized nature makes it resistant to hacking. Medical records stored on a blockchain ledger would be encrypted and distributed across a network of computers, making them much harder to tamper with compared to a traditional centralized database.
- Improved Data Sharing: Patients can control who has access to their medical data on a blockchain. This allows for secure and transparent sharing of information between authorized healthcare providers, streamlining care coordination and eliminating the need for patients to carry around copies of their records.
- Enhanced Transparency: Every change made to a patient’s data on a blockchain is logged and can’t be altered. This creates a clear audit trail, fostering trust and accountability within the healthcare system.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track the movement of medications, medical devices, and other supplies. This can help prevent counterfeit drugs from entering the system and ensure the quality and origin of products.
- Clinical Trials: Blockchain can be used to securely manage and track data from clinical trials. This can improve the accuracy and efficiency of trials, leading to faster development of new treatments.
There are also challenges to consider. Integrating blockchain technology into existing healthcare systems can be complex and make the system cumbersome as a result. Additionally, ensuring clear regulations and data ownership standards is crucial for widespread adoption.
However, blockchain has the potential to significantly improve the security, privacy, and efficiency of healthcare data management. As the technology matures and regulations evolve, we can expect to see more widespread use of blockchain in healthcare.
Expanded Reality
Expanded or Extended Reality (also known as XR) is a combination of various realities including
- Virtual Reality (VR) usually requires a headset and additional wearable equipment and provides an immersive experience but it isn’t linked to physical reality.
- Augmented Reality (AR) usually uses devices such as phones or tablets with a camera to integrate virtual objects into the real world.
- Mixed Reality (MR) adds interactive features to the AR like rotating objects to view them from different angles.
These three technologies are widely used in surgery to evaluate complex cases and design immersive surgical training procedures. MRI and X-ray are great diagnostic tools but they provide only an image that you can look at while extended reality can give the doctors an option to go inside the picture before they do it to the patient.
Imagine a future where…
Imagine a future where healthcare breaks free from physical limitations. The metaverse, a blooming digital space, is poised to revolutionize medicine with a blend of cutting-edge technologies. Here’s a glimpse of its transformative potential:
- Teleporting care: Distance won’t be a barrier. Doctors could hold immersive consultations and even perform virtual surgeries using advanced VR tools. Imagine a specialist in another country guiding a local surgeon through a complex procedure in real time!
- Revolutionizing training: Aspiring doctors can hone their skills in hyper-realistic simulations. Imagine practicing intricate surgeries on virtual patients in a safe, controlled environment before ever stepping into an operating room.
- Boosting mental health: The metaverse can create powerful therapeutic experiences. People with phobias could confront their fears in virtual environments, while others could find solace in supportive online communities.
- Personalized medicine: Digital twins, virtual replicas of patients, can be used to predict health risks and tailor treatments. Imagine a doctor using your digital twin to see how different medications would affect you before prescribing anything.
- Empowering patients: The metaverse can be a treasure trove of educational resources. Patients could access interactive guides on their conditions and participate in virtual support groups, becoming active participants in their own healthcare journey.
Of course, challenges like privacy and accessibility need to be addressed. But the potential of the metaverse to transform healthcare is undeniable. It’s a future where location melts away, replaced by a world of accessible, personalized, and immersive medical care.
Wondering about time-to-value?
Request a no-obligation discovery call and receive a preliminary estimate tailored to your KPIs.


