In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, digital solutions have become the superheroes we didn’t know we needed, revolutionizing how care is delivered and accessed. Thanks to the likes of telemedicine, electronic health records, and mobile health apps, patients can now enjoy VIP treatment from their couch, pajamas optional.
Healthcare providers are practically swimming in data, making decisions with the confidence of poker players holding a royal flush, all leading to patients feeling like winners too. Even better, these digital marvels help doctors and nurses chat more efficiently than a team in a multiplayer video game, breaking down traditional barriers and creating a healthcare adventure that’s as smooth as your favorite sitcom.
Here are a few statistics:
Market Size and Growth:
- Global Market Value: According to Statista, the global market for healthcare wearables was valued at USD 81.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 188.2 billion by 2028.
- Segment Breakdown: The market can be segmented by device type. Smartwatches and fitness trackers dominate the non-specialized category, while continuous glucose monitors (CGM) and smart patches are examples of specialized wearables.
User Adoption:
- Ownership Rates: A 2023 study by IDC suggests that one in three people globally will own a wearable device by 2024.
- Growth in Healthcare Applications: Research by MarketsandMarkets forecasts that the market for medical wearables specifically will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.3% from 2022 to 2027.
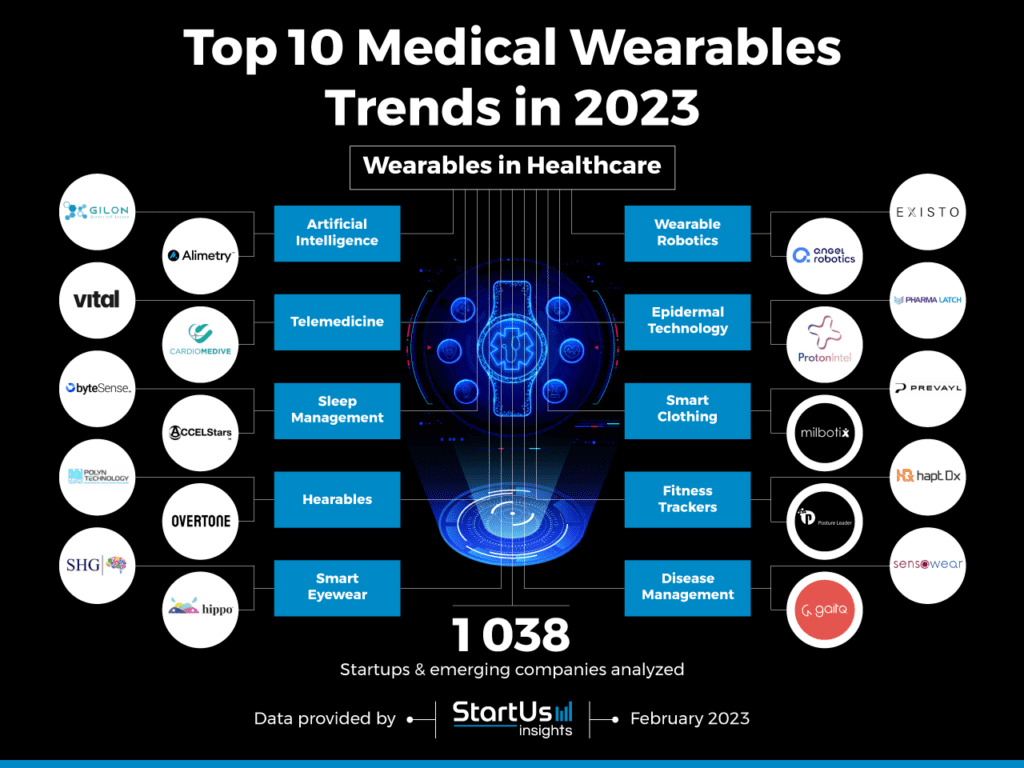
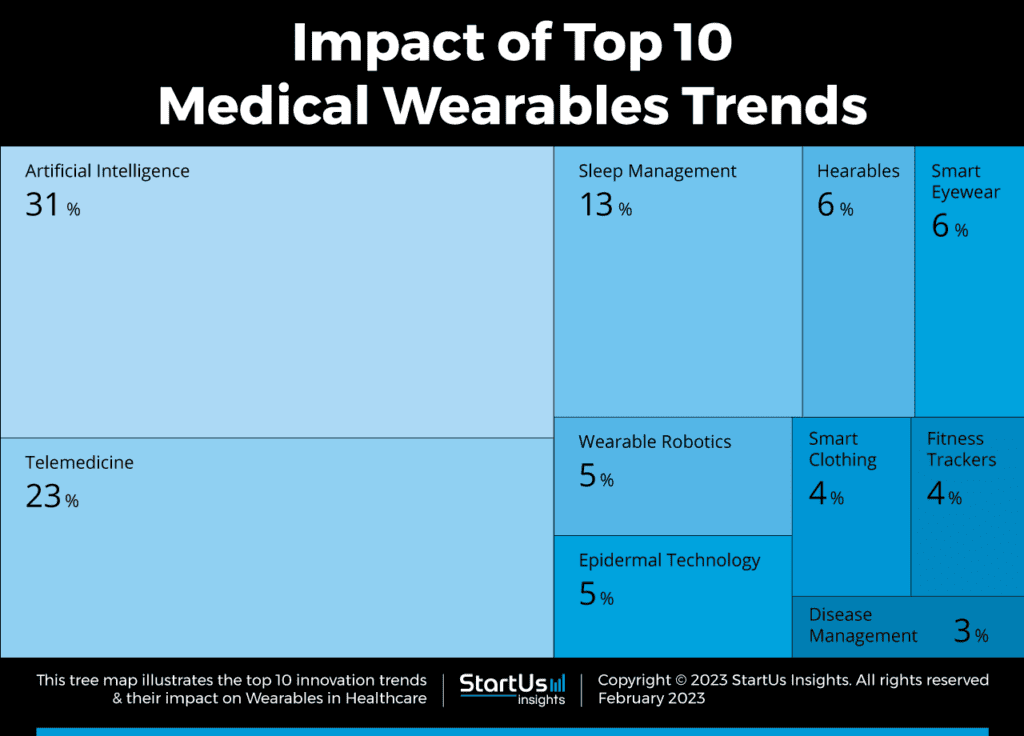
However, amidst this digital revolution, a crucial gap remains – the lack of clinical-grade digital health tools tailored to meet the rigorous demands of modern healthcare models.
While consumer devices like Fitbit and Apple Watch have paved the way for personal health tracking, they fall short when it comes to meeting the stringent standards required for clinical use. As healthcare continues to embrace digital innovation, there is an urgent need for tools that offer the same level of quality, reliability, and trust as traditional clinical-grade medical technology.
While consumer devices like Fitbit and Apple Watch have paved the way for personal health tracking, they fall short when it comes to meeting the stringent standards required for clinical use.
In this blog, we delve into the pressing need for clinical-grade digital health tools in today’s healthcare landscape. We explore the current state of digital health solutions, the demands for higher quality tools, the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead, and insights from industry leaders driving innovation in new care models.
Join us as we navigate the path towards closing the gap and advancing digital healthcare for all.
Digital Health Tools: Current Landscape
The healthcare industry is undergoing a digital revolution, with a surge of innovative tools transforming how we manage our health. This digital health landscape offers a variety of solutions, each with its unique strengths and considerations.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
This powerful duo is at the forefront of digital health advancements. Telemedicine allows patients to connect with healthcare providers virtually, facilitating consultations, diagnoses, and even prescription renewals from the comfort of their homes. This not only improves access to care, especially for those in remote locations or with mobility limitations but also reduces wait times and potentially lowers costs.
Remote monitoring complements telemedicine by using wearable devices and sensors to track vital signs, blood sugar levels, or other health indicators in real time. This continuous data stream empowers both patients and providers to proactively address health concerns and make informed treatment decisions.
Market Growth and Adoption:
- Global Market Size: According to a report by Grand View Research, the global telemedicine market reached a value of USD 81.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 400.5 billion by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.1%.
- Rising User Rates: A 2021 survey by McKinsey found that 55% of patients reported using telemedicine at least once, and 40% planned to continue using it after the pandemic. ([invalid URL removed])
- Remote Patient Monitoring Growth: CoachCare reports that RPM services and tools saw a 38x increase in use since 2020, highlighting the growing adoption of remote monitoring technologies.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Reimbursement Policies: Reimbursement policies for telemedicine services can vary across regions and insurance plans, which can be a barrier to wider adoption.
- Technological Barriers: Unequal access to technology and broadband internet can limit access to telemedicine for certain populations. For example, some
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive patient data transmitted through telemedicine platforms is crucial.
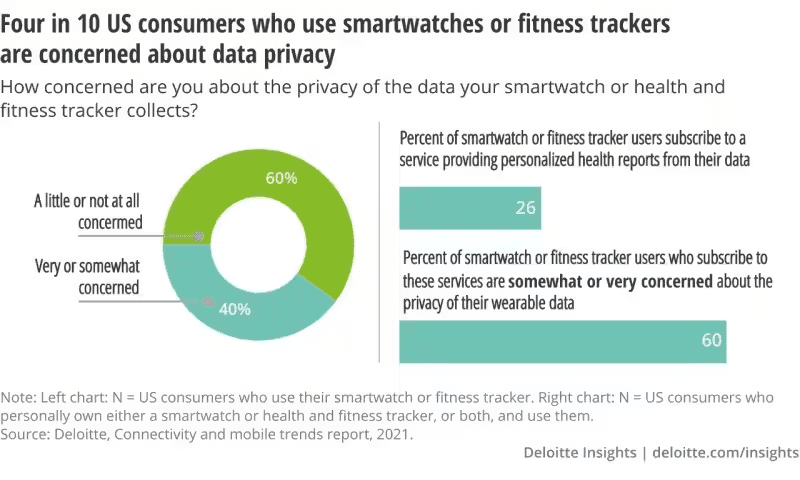
We wrote more on telemedicine, personalized healthcare, and other trends in our other article.
Home Hospitalization and Virtual Care
There is a phrase “Even walls are healing when you are at home.” Taking healthcare a step further, home hospitalization and virtual care programs enable patients to receive hospital-level treatment in the comfort of their own homes. It also helps to alleviate pressure on traditional hospital beds, especially during surges in patient volume.
This approach is ideal for patients recovering from certain surgeries or managing chronic conditions. Through remote monitoring and regular virtual consultations with healthcare professionals, patients receive the necessary care while recuperating in a familiar and often more comfortable environment.
This can not only improve patient satisfaction and outcomes but also alleviate the strain on traditional hospital resources. However, there are a few challenges along the way.
Clinical Outcomes and Effectiveness:
- Mortality Rates: A 2023 study published in Annals of Internal Medicine found that mortality rates for patients receiving care through home hospitalization programs were comparable to those in traditional hospital settings (around 0.5%).
- Reduced Readmission Rates: Some studies suggest that home hospitalization can lead to lower rates of hospital readmission compared to traditional care.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Limited Data: Long-term data on the cost-effectiveness and broader clinical outcomes of home hospitalization programs is still accumulating.
- Eligibility Criteria: Not all patients are suitable candidates for home hospitalization, and clear criteria need to be established to ensure patient safety and successful outcomes.
- Reimbursement Policies: Reimbursement models for home hospitalization services need to be established and standardized to incentivize wider adoption by healthcare providers.
Limitations of Consumer Devices
It’s also important to acknowledge that consumer-grade digital health devices, while convenient, may have limitations. The accuracy and functionality of these devices can vary depending on the manufacturer and intended use.
For example, a fitness tracker like the popular Apple watch, FitBit, or Garmin, is not as precise as a medical-grade blood pressure or heart rhythm monitor. Additionally, some devices that are more healthcare-oriented might require user calibration or come with complex interfaces that could be challenging for certain demographics.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine which devices are appropriate for your specific needs and to ensure proper use and interpretation of the data they provide.
The Call for Clinical-Grade Standards in Digital Health
The rapid innovation in digital health tools has undeniably improved healthcare accessibility and convenience. However, a critical question emerges: are these tools meeting the rigorous standards required for clinical settings? A growing chorus advocates for the implementation of clinical-grade standards in digital health.
This call for action stems from two main concerns.
- Firstly, there’s a quality gap between some consumer-grade devices and the tools traditionally used by healthcare professionals. These consumer devices may not deliver the same level of accuracy, reliability, or data security needed for making critical clinical decisions.
- Secondly, the current landscape of digital health tools needs to be better aligned with modern healthcare models. To truly integrate into established treatment protocols and workflows, these tools require robust interoperability and the ability to seamlessly share data with electronic health records (EHRs).
HUSPI has experience with integrating with EHR/EMRs... just saying. (Send us a message if you're curious.)
Implementing clinical-grade standards will ensure that digital health tools are held to the same high bar as traditional medical devices. This includes rigorous testing for accuracy, safety, and efficacy. Additionally, these standards should address data privacy and security concerns, protecting sensitive patient information. By establishing a clear framework, we can foster trust and confidence in the use of digital health tools within the medical community.
Ultimately, a focus on clinical-grade standards will pave the way for the responsible and effective integration of digital health tools into modern healthcare models. This will empower healthcare providers to leverage these advancements for better diagnoses, more personalized treatment plans, and ultimately, improved patient outcomes.
Challenges and Opportunities for Clinical-Grade Digital Health Tools
The push for clinical-grade digital health tools presents both challenges and exciting opportunities.
Challenges:
- Regulatory and Compliance Issues: Implementing clinical-grade standards necessitates navigating a complex web of regulations. Regulatory bodies need to adapt and streamline the approval process for these novel devices, striking a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring patient safety. Additionally, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations like HIPAA is crucial for building trust with patients and healthcare providers.
- Integration with Healthcare Systems: Integrating these new tools into existing healthcare systems can be complex. Hospitals and clinics may require upgrades to infrastructure and workflows to seamlessly integrate and utilize the data generated by these devices. Standardized communication protocols and interoperability between different devices are essential for smooth data exchange within the healthcare ecosystem.
Opportunities:
- Improved Patient Engagement: Clinical-grade digital health tools hold immense potential for improving patient engagement in their healthcare. These tools can empower patients to actively monitor their health metrics, track treatment progress, and participate in shared decision-making with their providers. Furthermore, educational and support resources readily available through these tools can enhance patient knowledge and overall well-being.
By addressing the challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities associated with clinical-grade digital health tools, we can usher in a new era of patient-centered, data-driven healthcare. This transformation will lead to improved quality of care, better health outcomes, and a more empowered and informed patient population.
What do Industry Leaders Say?
New Care Models:
The future of healthcare is about moving from episodic to continuous care. New care models will leverage technology to empower patients to manage their health proactively between doctor visits.
Eric Larsen, CEO of Omada Health (Digital chronic disease management)
We need care models that integrate physical and mental health, and that recognize the social determinants of health. Technology can play a crucial role in facilitating these integrated models.
Atul Gawande, Surgeon and Author
Enhancing Healthcare Delivery with Digital Tools:
Digital tools can automate tasks, improve data collection and analysis, and personalize treatment plans. This frees up healthcare professionals’ time to focus on complex cases and provide more holistic care.
Dr. Ruchira Barve, Chief Medical Officer at Alphabet’s Verily Life Sciences (Life sciences research)
Digital tools can democratize access to healthcare information and empower patients to make informed decisions about their health.
Dr. Anne Wojcicki, CEO of 23andMe (Genetic testing)
Strategies for Developing Quality Solutions:
Healthcare needs to prioritize the patient experience. Digital tools should be designed with user-friendliness and accessibility in mind.
Jeff Bezos, Founder of Amazon (Focus on customer experience)
Digital healthcare solutions need to demonstrate a clear return on investment. They should improve patient outcomes and reduce overall healthcare costs.
Dr. Lee Shapiro, Chairman of the Alliance for Health Reform (Focus on value-based care)
Future Directions and Recommendations
There are three major directions to focus on when we are talking about clinical-grade healthcare wearables and solutions. It’s their quality, collaboration, and innovation, as well as regulatory frameworks that would help with data security and other questions.
Investing in Quality Digital Health Tools:
- Focus on clinical-grade standards: Increased funding should be directed towards research and development of digital health tools that meet rigorous clinical standards for accuracy, safety, and efficacy.
- Public-private partnerships: Collaboration between government agencies, healthcare institutions, and technology companies can foster innovation and accelerate the development of high-quality digital health solutions.
- Value-based reimbursement models: Reimbursement structures should incentivize the use of digital tools that demonstrably improve patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
Encouraging Collaboration and Innovation:
- Open innovation platforms: Creating platforms for researchers, developers, and healthcare providers to share data and collaborate on digital health solutions can accelerate progress.
- Hackathons and innovation challenges: Sponsoring events that bring together diverse minds to tackle specific healthcare challenges can spark new ideas and lead to breakthrough technologies.
- Investing in digital health education: Training healthcare professionals on the latest digital tools and their integration into existing workflows is crucial for widespread adoption.
At HUSPI, we are very much interested in finding partners to use our software development skills in EHR/EMR integration as well as other projects to improve the digital healthcare industry.
Advocating for Supportive Regulatory Frameworks:
- Streamlined regulatory approval processes: Regulatory bodies need to adapt to accommodate the rapid pace of innovation in digital health while ensuring patient safety.
- Clear data privacy and security regulations: Establishing clear guidelines for data collection, storage, and access is essential for building trust within the healthcare ecosystem.
- Interoperability standards: Implementing standardized communication protocols between different digital health tools will ensure seamless data exchange and improve the integration of these tools within healthcare systems.
By prioritizing these recommendations, we can pave the way for a future where high-quality digital health tools are readily available, seamlessly integrated into healthcare delivery, and empower patients and providers to achieve better health outcomes.
This transformation requires a multi-pronged approach, with collaboration and innovation at its core, supported by strategic investments and a regulatory framework that fosters trust and facilitates progress.
Wondering about time-to-value?
Request a no-obligation discovery call and receive a preliminary estimate tailored to your KPIs.


