The world’s population continues to grow (as of summer 2023, there were 8,045,311,447 people living on the planet). While some rural areas have started to resurrect due to the post-pandemic realization that working in the office is not a critical requirement, still more people would love to move into the cities.
As a result, cities become more crowded and in dire need of updated and more efficient infrastructure and services. However, it’s hard to do some major overhauls in the existing real estate and infrastructure, therefore, there is a need for something more creative.
The Internet of Things (IoT) technologies come in handy in this case because they help to improve sustainability, livability, and efficiency. How? Let’s talk about that in today’s article.
Overall Picture
As we discussed in the previous article about sustainability, environmental concerns are gaining more and more traction and people want solutions that would help reduce the negative impact, while providing the same levels of comfort.
Data analytics and IoT come in handy for this purpose because they give the opportunity to measure everything and identify areas where usage (or excess) can be minimized. For example, this concerns smart energy systems (smart grids increase the reliability and security of the networks as well as protect from security threats) and waste management (monitoring garbage cans for example to optimize the waste collection schedules.)
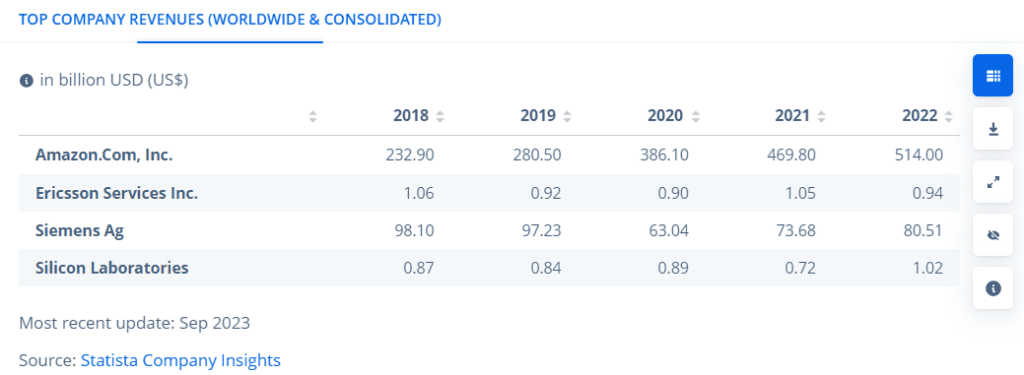
Numerous countries started to introduce smart city solutions on the government level as a result of the potential improvements for sustainable and economic growth. For example, Germany is to get EUR 1 billion investment from Siemens for urban technologies development and innovation. China also made the “Smart Cities Development Plan” a part of their Made in China 2025, an initiative that is aimed to take the Chinese market to a new level.
However, all these technologies have to take into account the existing infrastructure, and, as a result, not everything is as straightforward as it could’ve been. Let’s take a look at the challenges, restraints, opportunities, and market drivers for smart cities and technology innovations.
Not all economies are developed enough to provide appropriate infrastructure for smart cities. This includes legacy telecom connections that cannot provide low-latency and high-capacity connectivity and as a result, it is very difficult to introduce innovations that require high-speed internet for proper work.
Governments in developing and underdeveloped countries also lack appropriate budgets to upgrade the infrastructures required.
One of the major concerns in the area of smart city projects is privacy and security. The entire system is highly vulnerable since smart city solutions rely on IoT and central access points for different data. Considering the fact that data can include personal information or video/photo data, the issue of privacy and security of customers while adopting various identification systems has to be addressed holistically.
The advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies both accelerate the development of smart cities because they help to empower people, organizations, as well as systems to be more self-sufficient by acquiring and processing large amounts of data. With the help of insights from that data, people can make informed decisions without spending too much time on them.
For smart cities, AI and ML are vital for managing medical monitoring, industrial control systems, environmental sensors, traffic lights, smart meters, and others. With the help of data incoming from all these sources, it becomes easier to do predictive analysis and forecasts for smart city planning.
The fact that AI and ML are progressing at a geometric speed provides ample ground and opportunities for smart city development. Add to that the possibilities of new IoT sensors and solutions along with comprehensive big data analytics – and you get a really good technical ecosystem.
Smart City Market Statistics
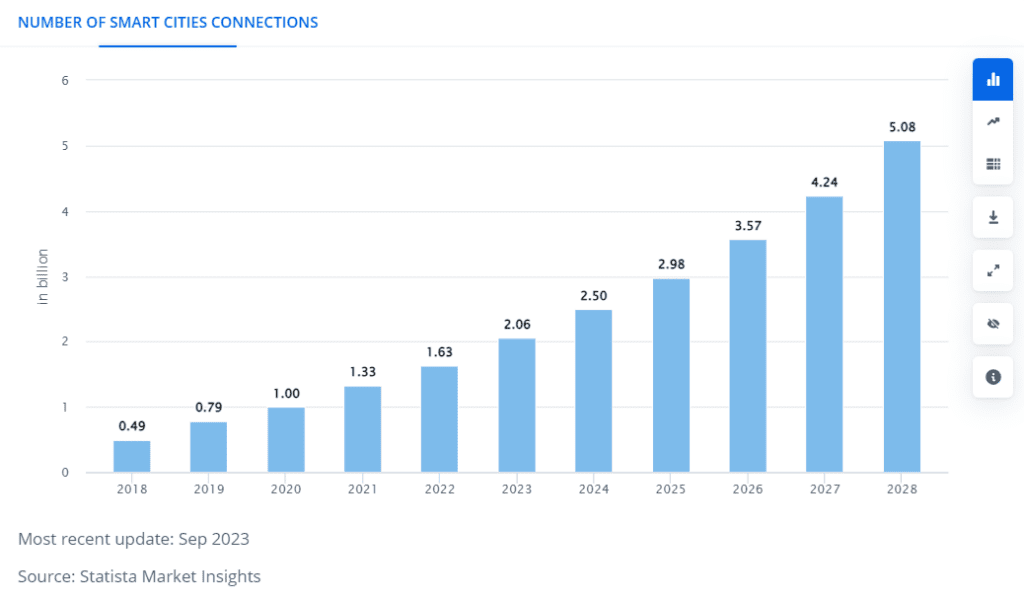
The COVID-19 period gave a boost to smart city development due to the fact that people had to become creative about meetings and managing things online without having physical contact. As a result, the projected revenue for the smart cities market in 2023 is projected to reach US $89.49 billion.
The further growth rate (CAGR) is expected to continue at 13.13%, according to Statista, which would lead to a market volume of US $165.80 billion by 2028.
The US is the global leader in terms of smart city revenues and it’s expected to generate US $11.12 billion in 2023. In the rest of the world, countries like South Korea and Singapore are leaders in implementing smart city solutions and initiatives.
Smart Cities Trends
IoT and Data-Driven Decision-Making
The Internet of Things (IoT) continues to play a central role in smart city development. IoT sensors and devices are used to collect data on various aspects of city life, such as traffic, air quality, energy usage, and waste management. This data is used to make informed decisions and improve city services.
In Europe and the USA, there are numerous initiatives and solutions existing at the moment.
United States:
- IBM Watson IoT: IBM offers a comprehensive IoT platform that includes device management, data analytics, and integration with AI capabilities through Watson.
- Microsoft Azure IoT: Microsoft’s Azure IoT suite provides a range of services for connecting and monitoring IoT devices, as well as tools for data analytics and machine learning.
- AWS IoT: Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a suite of IoT services, including device management, connectivity, and analytics through AWS IoT Analytics.
- Google Cloud IoT: Google Cloud provides a platform for connecting, managing, and processing data from IoT devices. It integrates with other Google Cloud services for advanced analytics.
- Cisco IoT Solutions: Cisco offers a variety of IoT solutions, including networking infrastructure, security, and analytics tools.
Europe:
- Siemens MindSphere: Siemens provides MindSphere, an open IoT operating system that connects products, plants, systems, and machines.
- Bosch IoT Suite: Bosch offers an IoT platform that includes device management, data analytics, and connectivity solutions.
- SAP Leonardo IoT: SAP provides the Leonardo IoT platform, integrating IoT data with business processes and analytics.
- Tele2 IoT: Tele2 offers IoT solutions for connectivity, device management, and data analytics.
- Schneider Electric EcoStruxure: Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure platform includes IoT solutions for various industries, focusing on energy management and automation.
- Vodafone IoT Solutions: Vodafone provides a range of IoT solutions, including connectivity, device management, and analytics services.
Sustainable Urban Planning
Smart cities are increasingly focused on sustainability and environmental considerations. This includes initiatives like renewable energy integration, waste reduction, and the promotion of green transportation options.
We wrote about real estate sustainability in the previous article.
Mobility Solutions
Smart cities are exploring innovative transportation solutions, including electric and autonomous vehicles, bike-sharing programs, and improved public transportation systems to reduce traffic congestion and improve mobility.
These solutions aim to enhance urban transportation, reduce congestion, and promote sustainable mobility. Here are a couple of examples from each region:
Europe:
- Amsterdam, Netherlands – Mobility as a Service (MaaS): Amsterdam has been a pioneer in implementing Mobility as a Service, an integrated approach to urban mobility that combines various modes of transportation into a single, accessible service. The city aims to make it easy for residents to plan and pay for their journeys using a single platform, incorporating public transport, bike-sharing, ride-sharing, and more.
- Barcelona, Spain – Superblocks: Barcelona has been developing the concept of “superblocks,” which involves transforming regular city blocks into pedestrian-friendly spaces. By restricting vehicle access to certain areas and promoting walking, cycling, and public transportation, Barcelona aims to improve air quality, reduce traffic noise, and create more livable urban spaces.

United States:
- Los Angeles, California – LA Express Park: LA Express Park is a smart parking management system implemented in downtown Los Angeles. It uses sensor technology to monitor parking space occupancy and adjusts parking meter rates dynamically based on demand. The goal is to optimize parking availability, reduce traffic congestion, and encourage the use of public transportation.
- Columbus, Ohio – Smart Columbus: Columbus has undertaken the Smart Columbus initiative to improve transportation in the city. The project includes the deployment of electric vehicle charging stations, the implementation of a connected vehicle platform, and the promotion of sustainable transportation options. It aims to enhance mobility, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and improve overall transportation infrastructure.
Digital Inclusion
Digital inclusion refers to the efforts to ensure that all individuals and communities, including those who are traditionally underserved or marginalized, have access to and the skills to use digital technologies. Here are examples of digital inclusion initiatives from various regions:
- Digital Literacy Programs:
- USA – EveryoneOn: EveryoneOn is a national nonprofit working to eliminate the digital divide by making high-speed, low-cost internet service and affordable computers accessible to all Americans. They also offer digital literacy training programs.
- UK – Good Things Foundation: This organization works to ensure that everyone benefits from digital technology. They run various digital inclusion programs, including online courses and community-based training, to help people develop digital skills.
- Community Wi-Fi Projects:
- India – Google Station: Google Station is an initiative that provides free Wi-Fi hotspots in public places, such as railway stations and bus stops. The project aims to bring affordable internet access to people in areas with limited connectivity.
- Brazil – Digital Social Inclusion Program: The Brazilian government has implemented programs to provide free internet access in public spaces, including schools and community centers, to promote digital inclusion.
- Affordable Hardware Initiatives:
- Africa – BRCK Education: BRCK Education is a company that focuses on providing rugged, low-cost hardware solutions designed for challenging environments in Africa. Their Kio Kit, for example, is a digital classroom in a box, aimed at improving education in low-resource settings.
- Global – One Laptop per Child (OLPC): OLPC is a non-profit organization that aims to provide low-cost, durable laptops to children in developing countries. The initiative seeks to bridge the digital divide in education.
- Government Initiatives for Inclusive Access:
- Australia – Digital Transformation Agency (DTA) – Digital Inclusion Strategy: The DTA in Australia has a Digital Inclusion Strategy that focuses on improving digital access and skills for all Australians, with a particular emphasis on vulnerable and disadvantaged groups.
- South Korea – Digital Inclusion Initiatives: South Korea has implemented various programs, including digital literacy training for seniors and low-income populations, to ensure that everyone can benefit from the country’s advanced digital infrastructure.
- Corporate Initiatives:
- Global – Facebook Connectivity Initiatives: Facebook has launched various initiatives, including the Connectivity Lab, to develop technologies like high-altitude drones and satellites to provide internet access to underserved regions around the world.
These examples showcase a range of strategies and approaches to promote digital inclusion, from providing access to affordable hardware and internet connectivity to offering digital literacy training programs. Digital inclusion is a multifaceted effort that often involves collaboration between governments, non-profit organizations, businesses, and communities.
Cybersecurity
As cities become more connected, the need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect critical infrastructure and citizen data is growing. Smart cities are investing in cybersecurity solutions and best practices.
United States:
- Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act (CISA): Enacted in 2015, CISA encourages the sharing of cybersecurity threat information between the government and private entities. It provides legal protections to companies that voluntarily share cyber threat indicators and defensive measures.
- Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA): FISMA, initially enacted in 2002 and subsequently updated, establishes a framework for securing federal government information systems. It requires federal agencies to develop, implement, and manage information security programs.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): While primarily focused on healthcare data privacy, HIPAA includes security provisions that mandate the protection of electronic protected health information (ePHI). Covered entities must implement safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of ePHI.
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA): GLBA includes provisions related to the security and protection of nonpublic personal information held by financial institutions. It requires these institutions to implement safeguards to protect customer information.
Europe:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Enforced in 2018, GDPR is a comprehensive data protection regulation that includes provisions related to the security of personal data. Organizations must implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure the security of personal data.
- Network and Information Systems Directive (NIS Directive): Implemented in 2018, the NIS Directive aims to enhance the cybersecurity capabilities of European Union member states. It requires operators of essential services and digital service providers to implement security measures and report significant incidents.
- Directive on Security of Network and Information Systems (NIS Directive 2): Proposed in 2021, this is a revised version of the NIS Directive aimed at strengthening cybersecurity in the EU. It introduces new requirements for cybersecurity incident reporting, cooperation, and security measures.
- ePrivacy Regulation: Still under discussion as of my last update, the ePrivacy Regulation aims to complement the GDPR by addressing electronic communications, including security aspects. It is intended to ensure the confidentiality and security of electronic communications data.
Smart Governance
The use of digital platforms and data analytics to improve the efficiency and transparency of city governance is becoming increasingly important. This includes e-governance initiatives and citizen engagement platforms.
United States:
- United States Digital Service (USDS): The USDS was established in 2014 to bring top technology talent into government and improve the delivery of digital services. It works on various projects to enhance the user experience of government websites, streamline processes, and address complex technology challenges.
- 18F: 18F is a government agency within the General Services Administration (GSA) that provides digital services to federal agencies. It works on projects focused on user-centered design, agile development, and open-source principles to create more efficient and effective government services.
- City Digital Alliance (CDA): CDA is a collaborative effort between the City of Chicago and technology companies to address urban challenges using technology. It focuses on projects related to transportation, water management, and other aspects of urban living.
Europe:
- Estonia – e-Government: Estonia is known for its advanced e-Government initiatives. The country has implemented a range of digital services, including e-Residency, which allows people to establish and manage businesses online, and the use of digital IDs for secure access to various services.
- United Kingdom – Government Digital Service (GDS): The GDS was established to transform the delivery of government services by making them simpler, clearer, and faster. It has led initiatives such as the redesign of government websites, the implementation of the Verify identity assurance system, and the promotion of agile and user-centered design methodologies.
- Barcelona, Spain – Smart City Initiatives: Barcelona has implemented various smart city initiatives, including the use of sensor networks for efficient waste management, smart street lighting, and the development of a digital platform for citizen engagement. These initiatives aim to enhance urban living and sustainability.
- Norway – Digitalization of Public Services: Norway has been actively digitalizing public services to improve efficiency and accessibility. This includes the use of digital platforms for citizen engagement, e-government services, and the implementation of technologies such as blockchain for secure and transparent transactions.
HUSPI has experience in developing e-government solutions.
Resilience Planning
Smart cities are preparing for the challenges posed by climate change and natural disasters by implementing resilient infrastructure and emergency response systems.
Smart Buildings
- Energy Efficiency: Smart building technologies continue to focus on optimizing energy use through systems like smart lighting, HVAC, and building automation. This reduces operational costs and environmental impact.
- Occupant Experience: Improving the comfort and productivity of building occupants is a key trend. Smart buildings use sensors and data analytics to create personalized and responsive environments, such as adjusting lighting and temperature based on occupancy.
- Health and Wellness: In light of the COVID-19 pandemic, there is a growing emphasis on air quality monitoring, touchless access controls, and other features that enhance the health and safety of building occupants.
- Sustainability Certification: Green building certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), are increasingly sought after as they reflect a commitment to sustainability.
- Smart Security: Smart buildings are adopting advanced security measures, including biometric access control, video analytics, and intrusion detection systems, to enhance safety and protect assets.
- Remote Building Management: With the growth of remote work and property management, smart building systems are becoming more accessible for remote monitoring and control through mobile apps and cloud-based platforms.
- Integration and Interoperability: Building systems are increasingly designed to be interoperable and integrate seamlessly, allowing for better coordination and data sharing between different systems (e.g., lighting, HVAC, security).
These trends indicate the ongoing evolution of smart cities and smart buildings to create more sustainable, efficient, and user-friendly urban environments. To stay updated on the latest trends, it’s essential to follow industry publications, attend conferences, and engage with experts in the field.
Wondering about time-to-value?
Request a no-obligation discovery call and receive a preliminary estimate tailored to your KPIs.