TL;DR: Push notifications in 2025 work best when they’re personalized, AI-driven, context-aware, and privacy-first. Less spam, more value — that’s the difference between an uninstall and becoming part of a user’s daily routine.
It’s pretty safe to say that most of us have a love/hate relationship with web and mobile push notifications. On the one hand, they’re super useful — they keep us updated on things we actually care about, whether it’s a new message, a payment reminder, or a sale alert. On the other hand, with the average smartphone user now receiving around 46 push notifications per day (yikes 🤯), it’s easy to feel overwhelmed and distracted.
Personally, I can’t stand seeing that little red dot in the top right corner of my iPhone apps. My friends laugh at me, but I can’t relax until I’ve cleared it – only then can I move on. And yet, I don’t want to turn notifications off completely, because I’d miss out on important updates.
This is why push notifications remain both a blessing and a curse. They can boost app engagement by up to 88%, but too many (or poorly timed ones) can just as quickly drive people to uninstall the app.
In this article, we’ll explore the types of push notifications, look at some real examples, and see how they work on iOS, Android, and the web — as well as what’s new in 2025.
Push Notifications — 2025 Statistics Spotlight
4.4% Average conversion rate
Typical push campaigns drive ~4.4% conversions across industries when targeting and timing are on point.
+56% Open rate with rich media
Adding images, GIFs, or video thumbnails can lift opens by ~56% vs plain text pushes.
Opt-out thresholds by weekly frequency
- 2–5 pushes/week → ~46% users opt out
- 6–10 pushes/week → ~32% opt out
Message fatigue kicks in fast. Keep cadence lean and value-dense.
77% Engaged last month
77% interacted with at least one push in the past month; 48% report making a purchase from a push.
3–10× Higher retention with push
Opt-in, thoughtful sequences correlate with materially higher 30–90 day retention.
Best time 8–9 am & 6–8 pm
Retail CTRs peak around morning/evening routines. Saturday underperforms; Mon–Tue usually best.
FinTech CTRs Benchmarks (2025)
- Android: ~2.84% CTR
- iOS: ~2.09% CTR
Varies by segment (personal finance, payments, trading) and personalization depth.
Tip: Push works best when it’s personalized, visually engaging, and not overused. Use frequency caps, quiet hours, and behavioral triggers.
What does Push Notification Mean?
Definition: A push notification is an automated message that is sent to the user by the server of the app that’s working in the background (i.e., not open.) Another way to describe it: a push notification is a message that’s displayed outside of the app.
Push notification is different from a pop-up you might see on a website or when you’re in a mobile app. Pop-ups are only activated if you’re using the app or website, whereas push notifications don’t require the app to be open.
There are also pull notifications, which are activated manually by the user. For example, on my phone, I check email manually, and push notifications are turned off because I want to check my email only at given times and not be constantly interrupted by ding-ding sounds.
- Push notifications: initiated by the central server or publisher.
- Pull notifications: initiated by the client or receiver.

The primary advantage of push notifications is the fact that, unlike email, push notifications don’t get trapped by spam filters. If they are configured correctly, push notifications can improve user retention and engagement ratio. However, if done wrong, they can appear so annoying and interruptive to the customers that instead of an increased engagement ratio, you’ll have an increased abandonment rate.
A few useful terms that you might see in this article:
- What is a notifications API? It is used to configure and display notifications to the user.
- What is a push API? It is the place where you subscribe to your app to the push service and get push messages from the service worker.
- A push notification service is a platform where you configure the notifications and send them out. We’ll talk a bit later about how a push notification service works.
A Brief History of Push Notifications
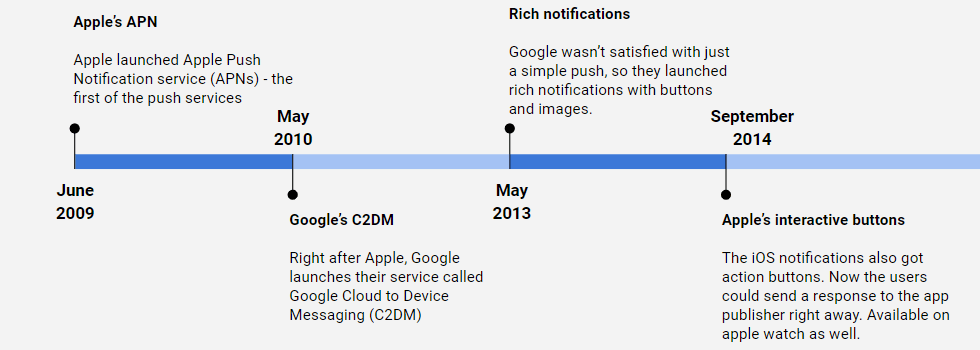
Apple and Google are the leaders in the push notifications feature.
In 2009, Apple launched the first-ever push notification service – Apple Push Notification Service (APN). Google didn’t stay behind for too long and launched its Cloud to Device Messaging service (C2DM) in 2010.
Rich notifications with images and calls to action appeared in 2013 on Google’s service, and then Apple added interactive buttons to its service in 2014.
In October 2014, Google acquired Firebase; it merged with Google’s push notification service and became known as Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM).
Types of Push Notifications
Types of Push Notifications by Purpose
Push notifications can be divided by purpose or by the device they are sent to.
By purpose, we can distinguish three main types of notifications:
- Transaction notifications. They are used to notify about events happening. For example, it can be a shopping update about a package or that an e-commerce transaction (paying for goods) was completed.
- System notifications. New product features announcements or holiday discounts fall under this category, along with notifications that, for example, you need to update your password on a website.
- User notifications. These notifications cause the most trouble and annoyance if they feel spammy. User ads inform about new messages, emails, or special offers from a website. These notifications require users to opt-in (or have an opportunity to opt-out).
There are three major types of push notifications based on the device.
Types of Push Notifications by Device
Types of Push Notifications by Device
🌐 Web
📲 Mobile
💻 Desktop
How does a web push notification work?
Web publications are a great instrument to allow users to opt in for updates from the website they visit. On the website owner’s side, web push messages allow re-engaging with the clients with relevant content.
When the user visits a website, it sends a message to the GCM push service. That, in turn, sends a request to the service worker on a web browser. These services check whether the user has signed up for the updates before.
If there is a relevant website update, the service workers also send push messages to those users who have already signed up for updates.
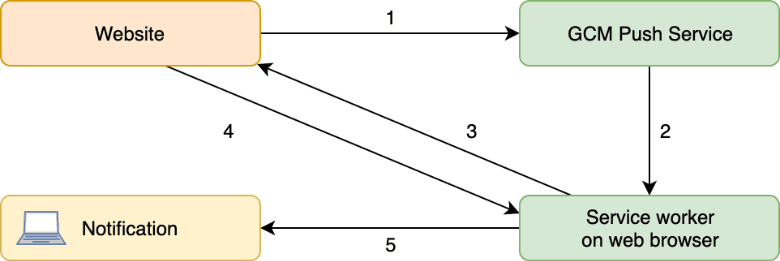
Web notifications are especially useful for social network platforms and news websites. You can also utilize them for e-commerce sites when you have a system of flash deals, for example.
How does mobile push notification work?
- How does push notification work in Android? On Android, the push notifications are sent (and received) by default.
- How does push notification work on iOS? On iOS, they are blocked by default. Therefore, you would need to opt-in your users. In the long run, this is more effective, especially considering the GDPR rules – you get the opt-in from the customer, which gets you on safe ground.
How does mobile users’ behavior differ on Android and iOS?
- Android: push notifications are on by system default, ergo Android phone users see the notifications more often, and they are more likely to open the notification message to see what’s inside.
- iOS: push notifications are off by default, and therefore iPhone users see fewer notifications. However, when they do get a notification, they open it much faster than Android users.
How to see Notification History on Android?
Android 11 introduced a new feature that allows users to check the notifications they have already dismissed. This is a useful thing for people like me who are easily annoyed by notifications. I often swipe them off the screen so I can focus on whatever I was doing, but sometimes, as I am already swiping them, I think “Oh, this actually might’ve been an important thing…”
Well, for Android users, push notification history is now also available. You have to turn the Notification history feature on prior to using it:
- Tap Notifications in the Settings app.
- Tap Advanced Settings.
- Tap Notification history.
- Tap the toggle to turn on the notification history feature.
- After you’ve turned it on, this is the place you will see all your dismissed notifications.
Most iOS mobile apps feature a standard message about notifications when the app is first opened after installation. However, if you change the wording there to make it look more enticing to stay up to date, the customers would be more responsive to it. Median opt-in rates range from 33% for games to up to 70% for travel & charity apps.
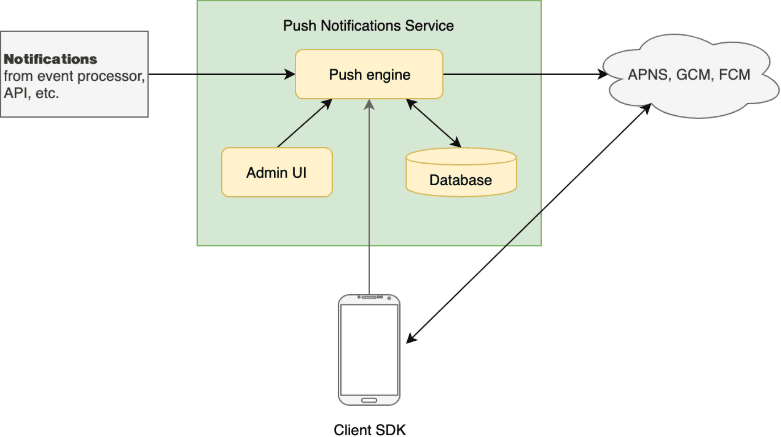
In terms of the actors involved in the process, there are three main ones:
- Push notification service (iOS, Android, Windows Phone, and FireOS all have their own services)
- App publisher (they enable the app with the push notification service)
- Client app (the app that gets the incoming notification)
How does a desktop push notification work?
Desktop notifications appear only on the users’ desktops. Unlike web notifications, these are driven mainly by the software installed on the computer.
Compared to web and mobile notifications, desktop notifications are more challenging to set up and require developers’ help.
Best Practices for Push Notifications (2025)
Do This Recommended
- Personalize messages with behavior, interests, and location to boost relevance and response.
- Time it right: retail CTRs typically peak around 8–9 am and 6–8 pm; Mondays/Tuesdays usually outperform weekends.
- Welcome early: onboarding pushes in the first 48 hours can lift 2-month retention substantially.
- Use rich media: images/GIFs/video thumbnails help messages stand out and improve opens.
- Segment & trigger: send based on real user actions (cart, content, milestones) instead of blanket blasts.
Watch Out For Caution
- Over-messaging: even 2–5 pushes/week can trigger heavy opt-outs; cap frequency and test cadence.
- One-size-fits-all: generic copy feels spammy; tailor to segments and lifecycle stage.
- Ignoring quiet hours: respect time zones and sleep/wake cycles; no 2 am surprises.
- Cluttered copy: keep it short, scannable, and value-first. One clear action beats three vague ones.
Retention Reality Check Evidence
Thoughtful, opt-in sequences correlate with stronger 30–90 day retention.
Early value + onboarding pushes help users form a habit fast.
Compared with ~5% / 4% for non-opt-in cohorts.
Bottom line: fewer, smarter, and better-timed notifications = happier users who stick around.
Types of Push Notifications by Business Cases & Purposes
There are several cases when your business can benefit from push notifications to your potential or existing customers:

Abandoned cart notification (“Hey, you’ve added this pink unicorn plush toy to your cart – would you like to proceed to checkout?”)

For-your-information (FYI) Notifications (“In case you’re wondering, those pink unicorn plush toys have been manufactured from organically-grown cotton.”)

Reminder Notifications (“Christmas is around the corner. Don’t forget about shopping for that pink unicorn plush toy.”)

Geolocation Notifications based on interests (“The store where you can purchase your pink unicorn is 5 feet away from you.”)

Time-bound Notifications (“You’ve got only 44 hours left to get the pink unicorn of your dreams before the price goes up.”)

Rich Push Notifications (“Pink unicorns – learn more about their production or purchase yours today.”)
Emerging Tech: What’s New in Push (2025)
AI “Companion” Push GenAI + Predictive
What it means for you: Use AI to tailor copy, timing, and next-best action so a push delivers instant value without extra taps.
Rich Media & Interactivity Images · Video · CTAs
What it means for you: Prefer rich templates and add a plain-text fallback so the message still works if media fails to load.
Context-Aware (Geo) Geofences & Triggers
What it means for you: Use geo as a value trigger (not just “you’re nearby”). Respect opt-in, OS limits, and quiet hours.
Omnichannel Platforms Push · Email · SMS · In-App
What it means for you: Orchestrate flows end-to-end: e.g., push → in-app tip → email recap if unopened.
MR Urgency Classifiers (PersoNo) LLM-powered
What it means for you: For AR/MR products, treat notification priority as a per-user model, not a fixed rule.
Smarter Timing (TIM) Temporal Models
What it means for you: Move beyond “best hour” heuristics; predict the next best slot per user and cap overlaps.
Privacy Focus (FCM) Minimize Metadata
What it means for you: Avoid sensitive payloads, encrypt where possible, and document data flows in your privacy policy.
What to do with push notifications?
Push notifications aren’t going anywhere — but they are changing. What started as simple “come back to the app” nudges is now evolving into something smarter, more personal, and more respectful of users’ time.
The future of push looks like this:
- Personalized messages that feel relevant instead of spammy
- AI-driven timing and content that adapts to each person’s behavior
- Context-rich delivery that takes into account location, activity, and even device state
- Privacy-conscious design that protects user data and avoids oversharing in payloads
In short, the best push notifications will feel less like interruptions and more like a helpful assistant in your pocket. When done right, they build trust, increase engagement, and make your app a part of someone’s daily routine — without being that annoying red dot you can’t ignore.
Need help with integrating a push notifications service into your business processes? HUSPI can help.
Wondering about time-to-value?
Request a no-obligation discovery call and receive a preliminary estimate tailored to your KPIs.
Sources & quick notes
- AI companion push & evolving expectations — OneSignal’s 2025 guidance: push should solve something on the surface; AI shapes timing and content. OneSignal
- Rich media & interactivity — Vendor docs confirm images, galleries, video, audio, buttons (platform-dependent). Braze Adobe Developer CleverTap
- Geolocation & context — Geofences and location triggers are standard; Apple Core Location docs and Braze geofence guides outline capabilities and constraints. Apple Developer Braze
- Omnichannel orchestration — Cross-channel personalization (push/email/SMS/in-app) is best practice in Braze docs; most platforms support it. Braze
- MR urgency classifier (PersoNo) — 2025 paper introduces a personalized LLM-based urgency model for MR; reports ~81.5% accuracy and highlights activity context. arXiv
- Smarter timing (TIM) — 2024 Temporal Interaction Model models user sequences and optimizes holistic send times, validated with A/B tests. arXiv ACM Digital Library
- Privacy & FCM — 2024 study of 21 secure messaging apps found metadata (and in some cases content) in FCM payloads, often undisclosed. Audit your payloads. arXiv


